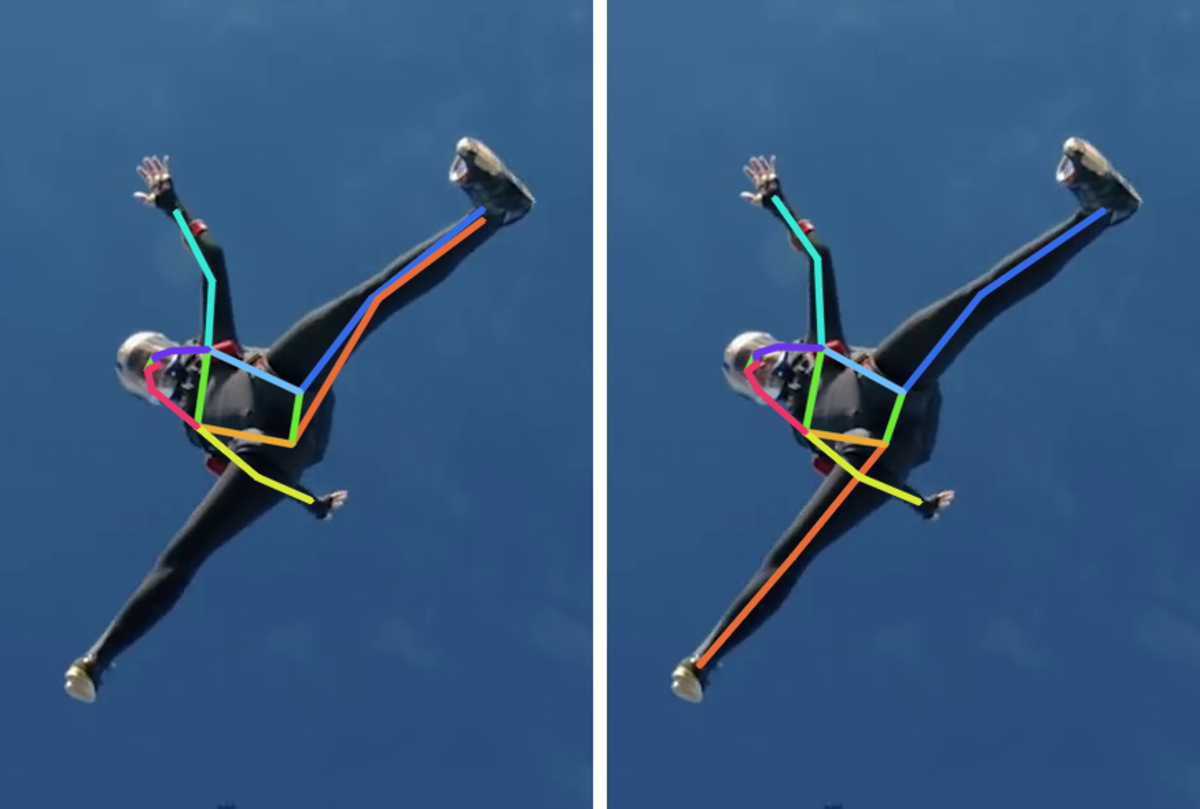
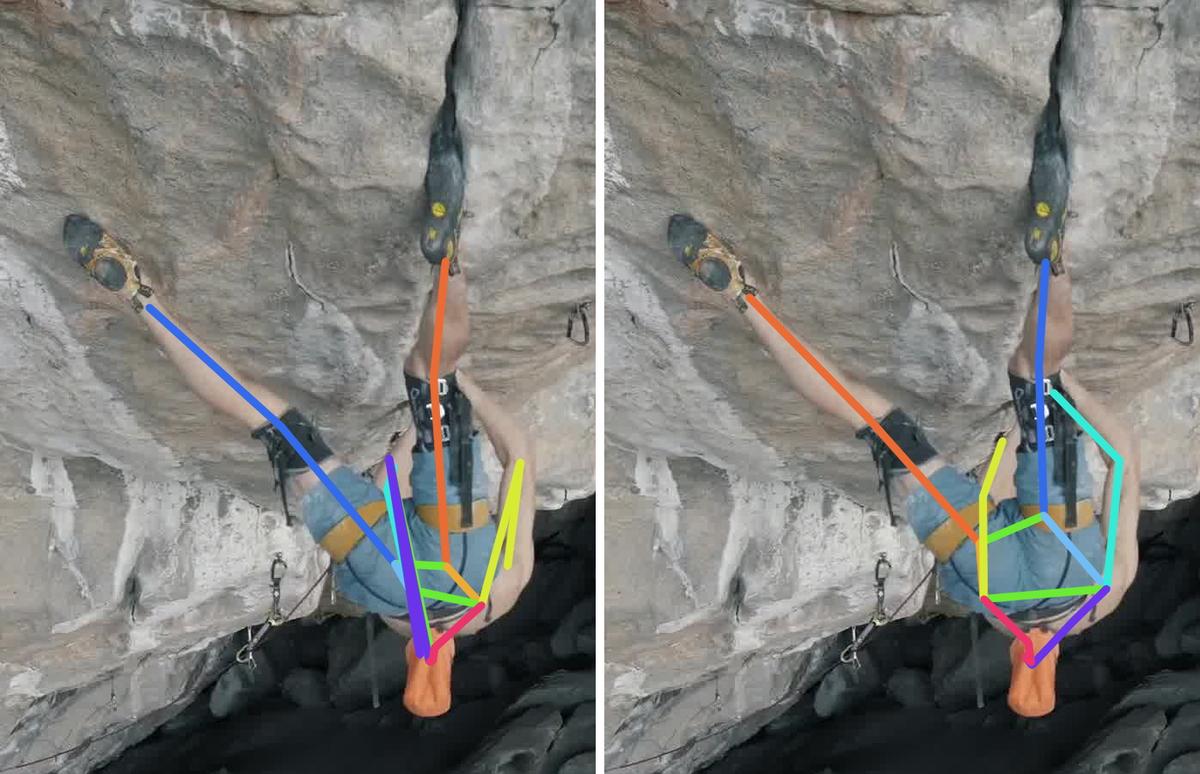
Results
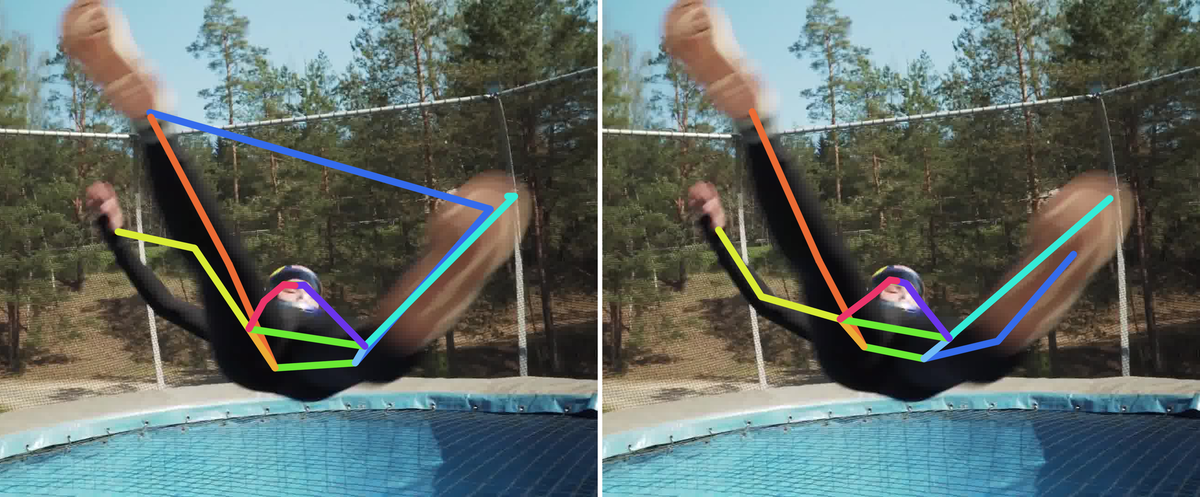
Comparison of the SOTA (ViTPose) trained on the COCO dataset and our method trained on the COCO dataset augmented with RePoGen images.
The limbs are: right arm, right leg, left arm and left leg.

First image description.
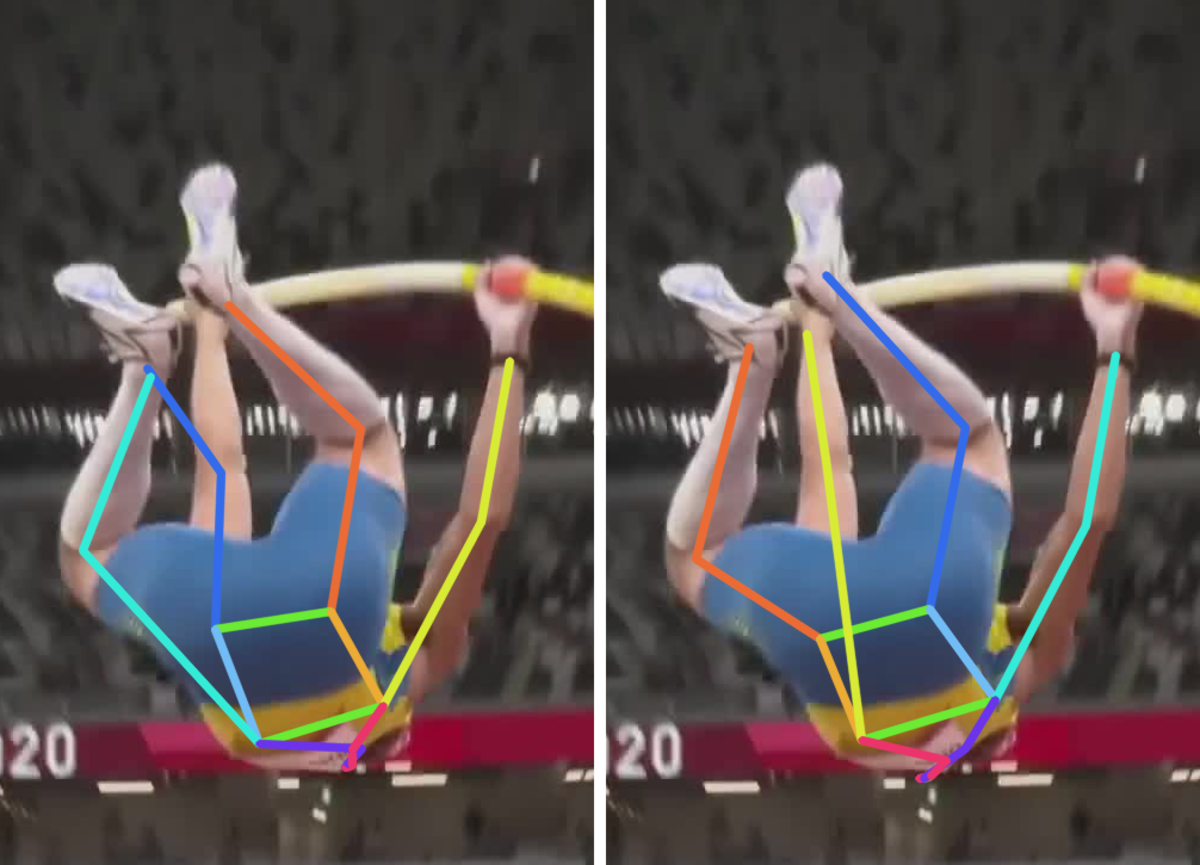
First image description.

First image description.
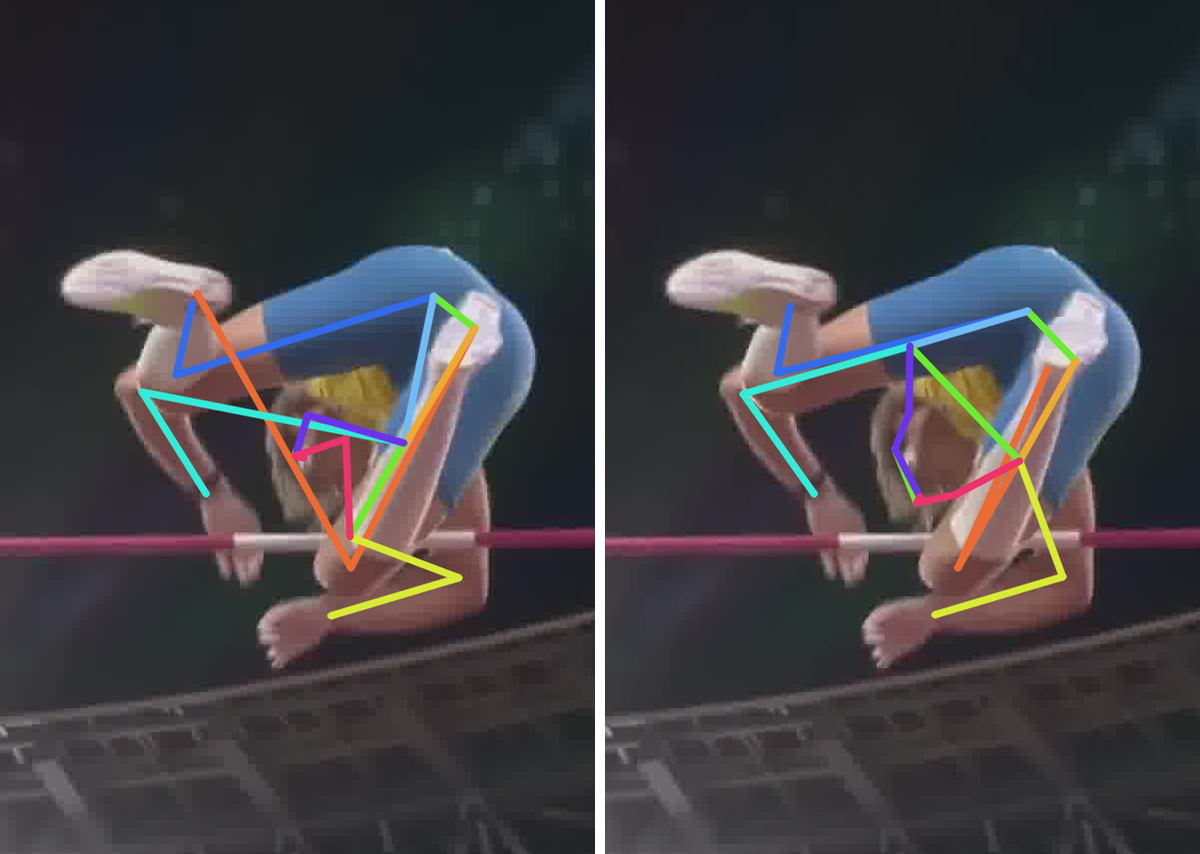
First image description.
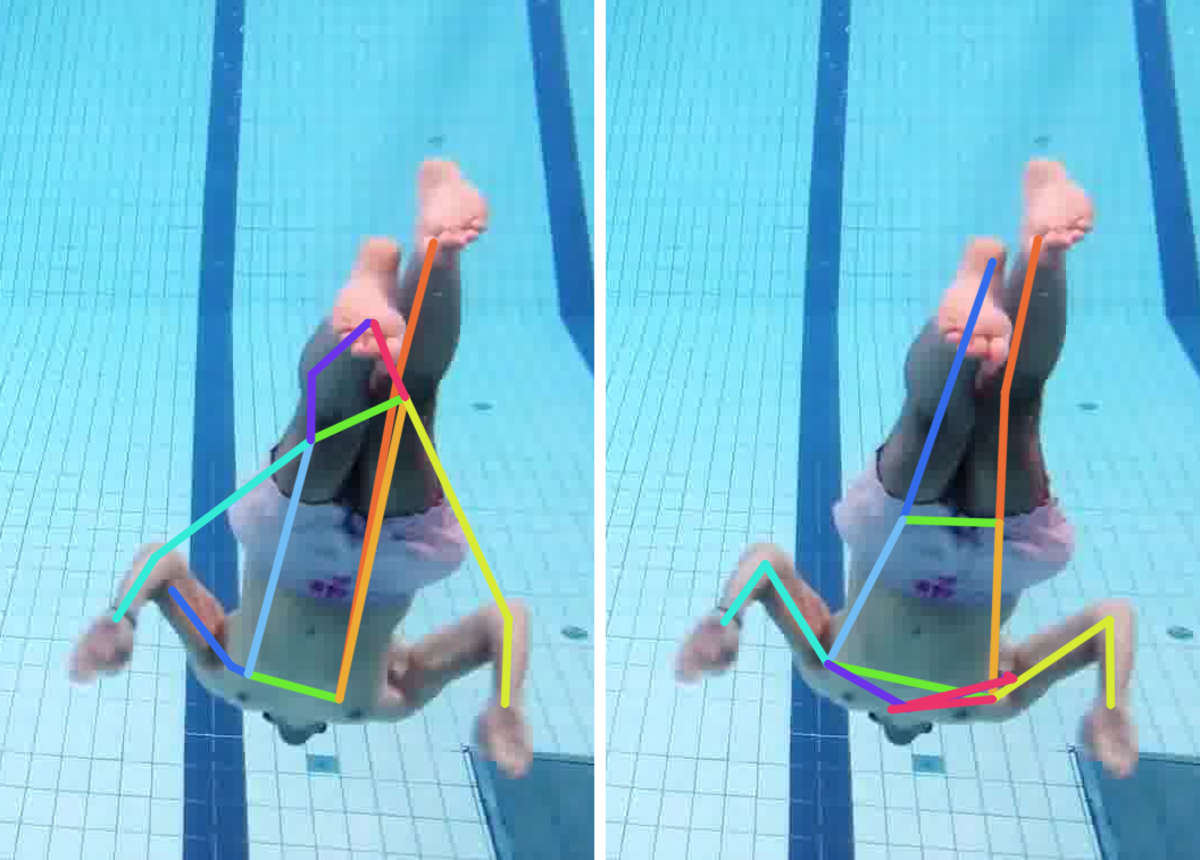
First image description.

First image description.
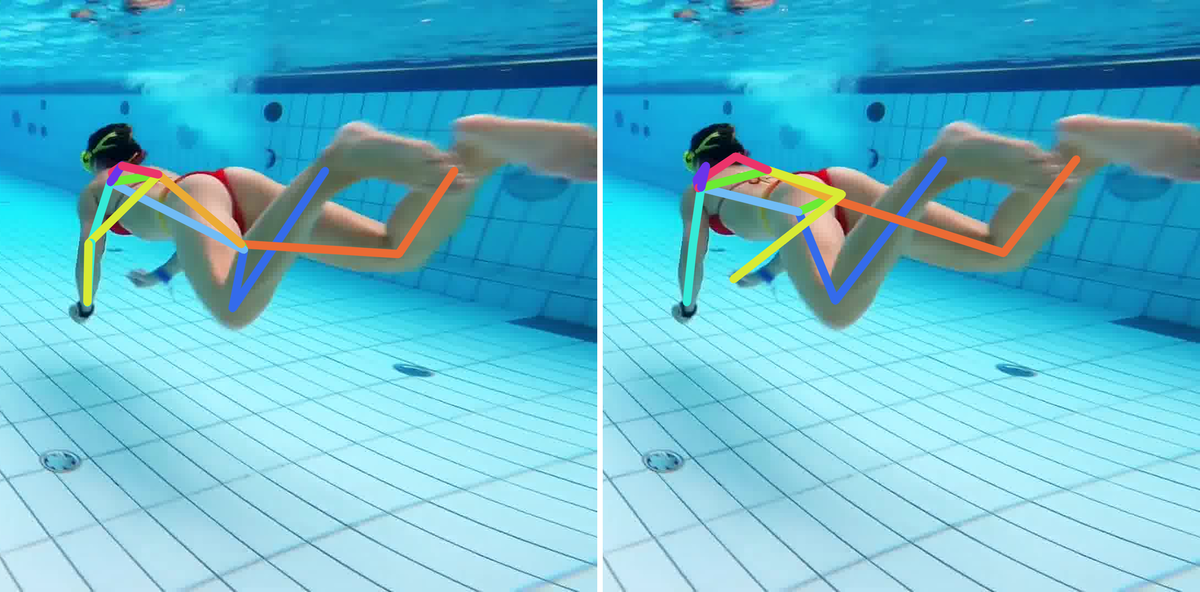
First image description.
First image description.
BibTeX
If you use our work, please cite it as follows:
@misc{purkrabek2023improving,
title={Improving 2D Human Pose Estimation in Rare Camera Views with Synthetic Data},
author={Miroslav Purkrabek and Jiri Matas},
year={2023},
eprint={2307.06737},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.CV}
}